Flat feet
OVERVIEW
What kind of disease is flatfoot?
Flatfoot is a type of foot deformity. Normally, the sole of the foot has a natural arch, but in flatfoot, the sole is mostly flat with an indistinct arch. It is generally believed that flatfoot is related to abnormal bone structure or lax muscles and ligaments, leading to the collapse of the medial longitudinal arch.
Flatfoot is common in children, especially preschoolers. In most cases, it is physiological, presenting as flexible flatfoot, and the condition tends to improve with age. In rare cases, flatfoot may be pathological, presenting as rigid flatfoot, often accompanied by pain.
For treatment, conservative approaches can be chosen for physiological flatfoot. Orthotic devices (such as insoles) designed based on biomechanics can help alleviate pain and improve gait. Very few cases of pathological flatfoot require surgical intervention.
Is flatfoot common?
Flatfoot is common in children, particularly preschoolers. It tends to improve as children grow. Among adolescents in China, the prevalence ranges from 25% to 49%, while among athletes, it can reach 11.7% to 39.5%.
SYMPTOMS
What are the types of flat feet?
Flat feet can be divided into flexible flat feet and rigid flat feet.
-
Flexible flat feet: This refers to the collapse or disappearance of the arch when standing under weight-bearing conditions, while the arch returns to normal when there is no weight load or when the foot is lifted. This type mostly occurs in infants and young children, primarily due to thick foot fat and weak muscle strength. It is usually physiological and does not require treatment, but orthotic devices (such as insoles) designed based on biomechanics can alleviate some foot symptoms.
-
Rigid flat feet: With rigid flat feet, the arch remains collapsed or absent regardless of whether the foot is weight-bearing or not. This type is mainly caused by abnormalities in the metatarsal, navicular, and cuneiform bones that form the arch, as well as their positional relationships. It is often accompanied by pain. In addition to conservative treatment, a very small number of cases may require surgical intervention after evaluation by a doctor.
What are the common symptoms and manifestations of flat feet?
Because flat feet have a larger contact area with the ground and lack the cushioning effect of the arch, prolonged walking or standing can lead to fatigue and pain, as well as abnormal gait or other functional impairments. Some patients may not experience any discomfort.
What are the risks of flat feet?
The feet play a crucial role in standing and walking.
-
Flat feet alter walking posture, causing excessive wear on the outer heel and inner sole, and making the heel more prone to injury.
-
During prolonged standing, walking, running, or jumping, the absence of proper arch support reduces shock absorption, leading to lower speed, endurance, and explosive power compared to normal feet. Fatigue and pain may occur in the feet, legs, waist, knees, and neck. The impact on the spine, brain, and internal organs may also lack cushioning, potentially causing damage.
-
Severe flat feet can lead to complications in other areas, such as degenerative changes and arthritis in foot joints (e.g., the subtalar joint), as well as stress fractures in the metatarsals, resulting in significant foot pain. In advanced stages, it may further affect the pelvis, causing tilting and rotation of the thigh and pelvic structure, downward displacement of the pelvis or coccyx, spinal curvature, and even shoulder imbalance.
CAUSES
What are the common causes of flat feet?
The causes of flat feet can be congenital or acquired.
-
Congenital factors: Include abnormal development of foot bones, ligaments, or muscles.
-
Acquired factors: Include infants standing or walking too early, prolonged weight-bearing standing, long-term bed rest, excessively high heels, foot diseases, and muscle imbalance caused by polio. Adult flat feet are mostly acquired, with the most common causes being posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and injuries to foot bones, joints, or ligaments.
Is flat feet hereditary?
If there is a family history of flat feet, the likelihood of a child developing flat feet during growth is significantly higher.
Why are flat feet more common in children?
- Infants are usually born with mild dorsiflexion and eversion of the feet.
- At 1 year old, due to abundant fat on the plantar surface and an underdeveloped longitudinal arch, almost all infants have flat feet as part of normal physiological development.
- By age 2, as plantar fat gradually disappears and eversion decreases, the longitudinal and transverse arches become more pronounced.
- Around age 10, the foot arch typically returns to normal.
Therefore, the younger the age, the higher the incidence of flat feet, but children's flat feet often improve with age.
DIAGNOSIS
How to Diagnose Flat Feet?
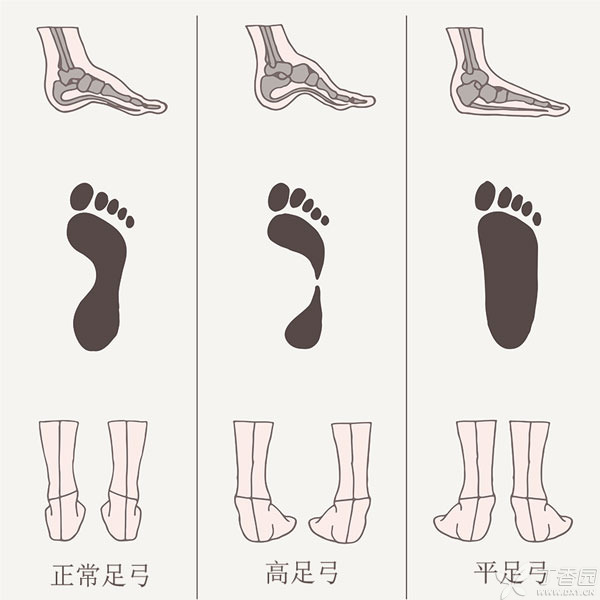
The human foot can be divided into three basic types: flat arch, normal arch, and high arch.
There is a simple way to determine your foot arch type—wet the sole of your foot, step on the ground, and examine the footprint:
- If most of the footprint is visible, it may indicate a low arch or flat arch;
- If about half of the footprint is visible, it may suggest a high arch.
To confirm flat feet, a doctor must conduct a physical examination, review the patient's medical history, and perform X-ray imaging.
What Tests Are Needed for Flat Feet Diagnosis?
Footprint analysis and X-ray imaging are the primary diagnostic methods, which can complement each other:
-
Footprint Analysis: By measuring the footprint, the foot can be classified, and the height of the medial arch and the degree of heel valgus can be evaluated. Common methods include mirrored photo footprints and plantar pressure detection. This method is simple, efficient, and cost-effective.
-
X-ray Imaging: Weight-bearing X-ray measurements of the foot can diagnose and assess flat foot deformities. X-ray measurements are more accurate but also more expensive.
TREATMENT
When should flat feet require medical attention?
If flat feet are accompanied by pain, it is necessary to visit a pediatric orthopedics or orthopedic specialist for a comprehensive evaluation. Additionally, abnormal gait, recurrent ankle sprains, back pain, leg length discrepancy, or even scoliosis may also be related to flat feet. Treatment may include muscle and tendon stretching exercises, custom orthotic insoles, or surgical intervention if necessary.
Which department should be consulted for flat feet?
Pediatric orthopedics or orthopedics.
Do flat feet always require treatment?
Not necessarily.
- Flexible flat feet account for over 95% of cases, and the vast majority are asymptomatic, representing a normal physiological variation. In such cases, the foot's structures are essentially normal, and no treatment is needed.
- Rigid flat feet are less common and are usually associated with skeletal deformities or neurovascular conditions. These cases often involve structural abnormalities and require medical evaluation and intervention.
How are flat feet treated?
-
Asymptomatic flat feet are considered physiological rather than pathological and do not require treatment.
-
Symptomatic flexible flat feet can initially be managed with exercises, appropriate footwear, and orthotic devices.
-
If conservative treatments fail for rigid flat feet, surgical options such as osteotomy, arthrodesis, or joint stabilization may be considered. Surgery aims to relieve symptoms, prevent permanent deformity, and improve quality of life.
Can flat feet be completely cured?
While most cases of flat feet cannot be fully cured through conservative treatments, symptoms can be effectively alleviated.
Surgery is the last resort for pediatric flat feet and can help prevent permanent deformities.
How can flat feet be managed with home rehabilitation exercises?
Functional flat feet can be corrected with the following rehabilitation exercises:
Plantar fascia release (G6)
Use a tennis ball or foam roller to massage and relax the foot arch, restoring normal muscle and fascia tension.
Strength and functional training: Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the arch, establish proper foot movement patterns, and improve lower limb function.
- Toe towel scrunches
- Resisted foot inversion with a resistance band
- Big toe lifts
- Resisted dorsiflexion with a resistance band
- Single-leg stance: Although flat feet may seem to increase contact with the ground, the lack of arch structure often leads to poor balance. Single-leg stance exercises can improve stability, progressing to eyes-closed single-leg stance.
- Soft surface or sand walking: Correct walking patterns by landing on the outer heel first, rolling through the outer arch to the forefoot, and pushing off with the big toe. Barefoot walking on soft surfaces or sand enhances foot sensation and ankle stability.
Stretching exercises
Stretch tight lower limb muscles after daily activities or rehabilitation to restore normal length and prevent fatigue.
- Calf (posterior) muscle stretch
- Anterior tibialis stretch
Do flat feet require orthotic insoles?
Orthotic insoles are recommended for younger patients, those with severe symptoms, or individuals who frequently stand, walk, or run.
Patients should visit a professional orthotics facility for foot measurements and custom insoles. Orthotics provide arch support, improve weight distribution, and reduce pain or injury risk.
However, orthotics do not cure flat feet—they only alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. To address the root cause, rehabilitation exercises are essential to strengthen arch-supporting muscles and establish proper foot mechanics.
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What should flat-footed patients pay attention to in their diet?
No special precautions are needed; a normal diet is sufficient.
What should flat-footed patients pay attention to in daily life?
First, encourage regular exercise with varied methods, primarily aimed at strengthening foot muscles and ligaments and promoting arch development.
- Heel raises can increase calf muscle strength, improve ankle stability, and alleviate flat-foot symptoms.
- Calf stretches with toe pulls mainly target the posterior calf muscles, aiding in calf shaping and relieving flat-foot symptoms.
- Additionally, activities like barefoot walking, stretching the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, and toe-gripping exercises to train small foot muscles can be beneficial.
Second, correct poor postures, such as W-sitting.
Lastly, short-term use of custom foot orthotics, including various insoles, orthopedic shoes, and medial arch supports, can significantly improve foot pain and balance.
How should family members care for someone with flat feet?
The main focus is on scientific education, teaching them the difference between physiological variations and disease. Not all flat feet require treatment, especially for children with flexible flat feet, as symptoms often lessen with age.
PREVENTION
Can Flat Feet Be Prevented? How to Prevent It?
The exact causes of flat feet are not yet fully understood, but the following risk factors can be controlled to reduce or avoid flat feet.
-
Control weight. Obesity may increase the risk of flat feet by 50%.
-
Avoid frequent W-sitting. Habitual W-sitting is strongly associated with bilateral flat feet in children.
-
Go barefoot when possible. Children accustomed to wearing shoes have a significantly higher incidence of flat feet compared to barefoot children, and closed-toe shoes lead to higher rates than open-toe sandals or flip-flops. This suggests that walking barefoot strengthens muscle power and mobility, promoting arch development.